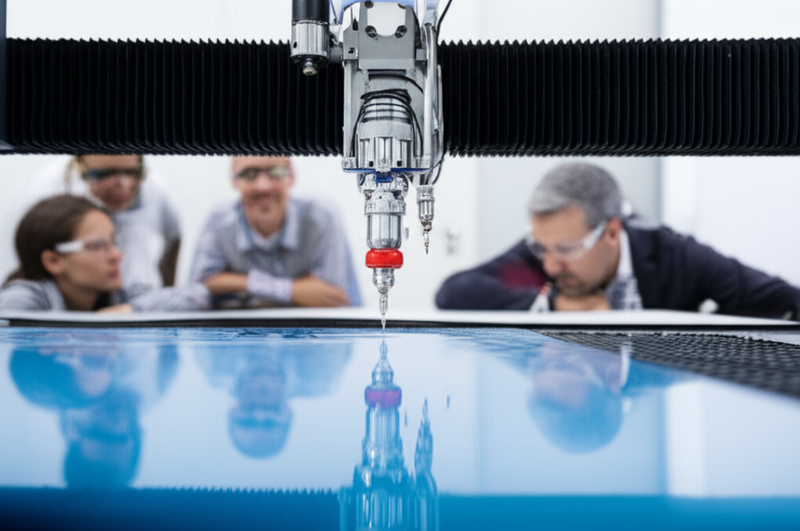
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for water jet cutting machine cost
Global manufacturers and fabricators are increasingly turning to water jet cutting technology for its exceptional precision, material versatility, and clean, cold-cutting process. However, for B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the true cost of acquiring and running a water jet cutting machine is pivotal—not only for budgeting purposes but also for maintaining competitiveness amid shifting economic conditions and global supply chain complexities.
The cost of a water jet cutting machine extends far beyond the initial purchase price. Decision-makers must evaluate depreciation, consumables, labor, energy consumption, and maintenance, all of which can vary significantly depending on regional market dynamics and operational requirements. For businesses in emerging or fast-growth markets such as South Africa or Turkey, where import duties, currency fluctuations, and sourcing logistics introduce additional variables, a clear, actionable grasp of the complete cost structure is crucial to making sustainable capital investments.
This comprehensive guide demystifies the landscape by covering:
– Water jet machine types (including pure water, abrasive, CNC, robotic, and portable systems)
– Material compatibility and application sectors that shape value propositions across industries
– Manufacturing quality and quality control considerations to ensure machinery reliability and long-term ROI
– Supplier qualification and vetting strategies to streamline international sourcing and risk minimization
– Detailed cost breakdowns—from acquisition and operation to total cost of ownership and hidden expenses
– Market analysis and best sourcing practices tailored for global regions, with insights into local challenges and opportunities
– Direct answers to frequently asked buyer questions to resolve common pain points and support confident negotiations
With practical analysis and actionable advice, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed, future-proof sourcing decisions—enabling organizations to optimize their investment, maximize production efficiency, and build resilient supplier relationships in the evolving global market for water jet cutting technology.
Understanding water jet cutting machine cost Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Water Jet Cutting | Uses only ultra-high-pressure water, no abrasives | Cutting soft/non-metallic materials: food, foam, textiles | Lower running cost & maintenance; cannot cut hard materials; best for specialized sectors |
| Abrasive Water Jet Cutting | Adds abrasive (usually garnet) to high-pressure water | Metal, stone, ceramic, glass, aerospace, general industry | Versatile for tough/thick material; higher consumable/maintenance costs; requires reliable abrasive supply |
| 3-Axis CNC Water Jet Cutter | Gantry or cantilever CNC control (flat/horizontal cutting) | Metal sheets, glass, plate processing, signage, machining | Predictable, cost-effective for flat parts; not for 3D/complex shapes |
| 5/6-Axis Robotic Water Jet | Multi-axis robot—complex 3D motion & multi-angle cutting | Automotive interiors, aerospace, intricate fabrication | Flexible for 3D/intricate jobs; highest upfront/system cost; more complex integration |
| Portable/Compact Water Jet | Mobile, small footprint, transportable | On-site/remote repairs, construction, prototyping | Rapid deployment, low space needs; limited power & cut thickness, not for high-volume production |
Pure Water Jet Cutting
Pure water jet cutting systems are engineered for processing materials that do not require abrasive action, such as rubber, foam, paper, textiles, and specific food products. These machines excel in industries demanding clean, precise, and heat-free cuts, which is particularly valuable for hygiene-critical sectors. From a B2B perspective, buyers are drawn to these machines for their lower upfront and operating costs, ease of maintenance, and simpler operator training. However, the limited material compatibility often restricts ROI to businesses with sufficient application volume in soft materials, so careful assessment of end-use trends is critical.
Abrasive Water Jet Cutting
Abrasive water jet cutters integrate abrasive particles into the water stream to break down hard materials, enabling precision cutting across metals, ceramics, stone, and composites. This versatility makes them indispensable in sectors like aerospace, automotive, construction, and heavy manufacturing. B2B buyers should weigh increased total cost of ownership due to higher consumable and maintenance expenditures, particularly in regions where abrasive supply chains may be inconsistent. Buyers from Africa, South America, or emerging industrial hubs should also prioritize robust technical support and local consumable sourcing to ensure long-term operational reliability.
3-Axis CNC Water Jet Cutter
3-axis CNC water jets are designed to automate straight-line and profile cuts on flat sheets and plates, commonly using a gantry or cantilever architecture. Their straightforward mechanics and predictable programming reduce operator error and training time, making them attractive for high-throughput, standardized fabrication environments, such as metal service centers or glass shops. For B2B buyers—especially those with consistent product lines—these systems offer an advantageous balance of investment and productivity. However, their inability to handle three-dimensional parts means buyers must carefully analyze future expansion needs before purchase.
5/6-Axis Robotic Water Jet
These advanced machines employ an articulated robotic arm for multi-directional, 3D part cutting—enabling intricate shapes, complex geometries, and undercuts across diverse materials. Sectors like automotive (e.g., dashboard trimming), aerospace (composite structures), and custom engineering or prototyping benefit significantly from this capability. For B2B buyers with rapidly changing product demands or custom work, the flexibility and precision offset the substantially higher acquisition and integration costs. Considerations should include availability of skilled technicians, system interoperability, and the anticipated lifecycle of the machinery.
Portable/Compact Water Jet
Portable and compact water jet cutters are tailored for mobility—serving onsite maintenance, remote construction, or quick-turn emergency repairs where bringing in large panels is impractical or time-sensitive. These systems are particularly valuable for B2B buyers in construction, mining, oil & gas, or any fieldwork-centric industry with variable job sites. While they offer the benefits of fast deployment and minimal space requirements, their lower cutting power and limitations on material thickness or part size mean they supplement, rather than replace, full-scale production systems. Supply chain reliability for parts and service at remote locations should be a core purchasing consideration.
Related Video: Fast Extreme Water Jet Cutter Machine Working, Modern Technology Waterjet Cutting Compilation
Key Industrial Applications of water jet cutting machine cost
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of water jet cutting machine cost | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Fabrication | Precision cutting of steel, stainless, aluminum, and alloys for machinery parts | High precision, no heat-affected zone (HAZ), flexible for prototyping and mass production | Machine reliability, abrasive supply logistics, after-sales support |
| Construction & Stone Processing | Shaping of marble, granite, ceramics, architectural glass | Intricate designs with minimal material waste, maintains material integrity | Local service availability, water/abrasive quality, machine size |
| Automotive & Aerospace | Cutting of composites, aluminum, and specialty metals for components | Delivers tight tolerances, supports advanced lightweight materials | Advanced CNC integration, global parts sourcing, operator training |
| Electronics & Electrical | Cutting of insulators, circuit materials, and high-purity plastics | Non-contaminating, micro-precision; essential for cleanrooms | Precision control, clean cutting environment, maintenance cycle |
| Food Processing | Cutting of hygienic packaging, rubber or foam for conveyor and gaskets | No thermal damage, ensures sanitary cuts, fast changeover | Food-grade certification, energy efficiency, compliance with local regulations |
Insights into Sector-Specific Use Cases
Metal Fabrication
Water jet cutting is widely deployed in metal fabrication facilities for the precise cutting of various metals into custom shapes or complex components. The hourly operational cost—factoring in machine depreciation, consumables, and labor—directly impacts pricing strategies for B2B contracts and tenders. Buyers in markets like South Africa or Turkey must focus on sourcing robust machines with predictable maintenance cycles. Ready access to abrasives and technical support are essential for minimizing downtime and controlling TCO (total cost of ownership), especially in regions where import lead times may be prolonged.
Construction & Stone Processing
Architects and builders frequently rely on water jet cutting for detailed shaping of marble, engineered stone, ceramic, and specialty glass. The cost per hour becomes a crucial part of project budgeting, as intricate or high-volume work demands reliable performance and material efficiency. In countries such as the UAE or Brazil, where local climate may influence water and abrasive quality, it’s advisable to specify machines with efficient water filtration and local after-sales support. Machine footprint and compatibility with available utilities can further impact long-term cost-effectiveness.
Automotive & Aerospace
In the automotive and aerospace sectors, water jet cutters are used for critical tasks such as cutting lightweight composites, titanium, and aluminum alloys. Here, the operational cost is balanced against the need for rapid prototyping, flexibility in design changes, and compliance with stringent international standards (e.g., ISO, AS9100). B2B buyers from Germany or Turkey should prioritize machines with advanced CNC capabilities and ensure global sourcing for spare parts and abrasive supply, supporting incoming design updates and minimizing lead times for urgent projects.
Electronics & Electrical
For electronics manufacturers, clean, precise, non-contaminating cuts are necessary—especially in applications like circuit insulation, cleanroom sealing, or high-purity plastics for connectors. Water jet cutting’s running cost is relatively low due to minimal secondary processing, but sourcing considerations shift towards machines capable of micro-cutting and with optimized maintenance for high uptime. Buyers in rapidly industrializing economies should verify that suppliers offer both technical training and consistent consumable quality.
Food Processing
In food and packaging sectors, water jet machines deliver hygienic, heat-free cutting of foamed materials, gasket rubbers, or specialty hygiene packaging that must remain uncontaminated. The machine cost is justified by operational efficiency and regulatory compliance (e.g., food-grade components, wash-down capability). For businesses in Egypt or Spain, sourcing considerations include local certification requirements, machine efficiency, and readiness for multi-shift operations in demanding environments. Access to warranted after-sales and documentation for audits is also paramount.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for water jet cutting machine cost
Selecting Materials for Water Jet Cutting Machines: B2B Considerations and Cost Implications
Selecting the right construction materials for water jet cutting machines directly influences performance, longevity, operating costs, and regulatory compliance. For international B2B buyers—especially in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—factoring in local conditions (water quality, climate), supply chain accessibility, and compliance with standards such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS is essential for maximizing ROI and minimizing operational risks. Below, we analyze stainless steel, carbon steel, specialty alloys (e.g., Inconel), and reinforced polymers as commonly used machine and component materials relevant to water jet cutting machine costs.
Stainless Steel (e.g., 304/316)
Key Properties:
Stainless steel alloys, such as 304 and 316, are revered for their resistance to corrosion, particularly in humid, saline, or chemically aggressive environments. They offer excellent structural strength, high temperature and pressure tolerance, and are easily fabricated to exact tolerances, which is crucial for water jet components exposed to constant high-pressure streams and abrasive slurries.
Pros:
– Outstanding corrosion resistance, even in variable water qualities.
– High mechanical durability—minimizing unplanned downtimes due to failure.
– Global availability and acceptance; readily meets ASTM A240, DIN 1.4301/1.4404, JIS G4303 for industrial use.
Cons:
– Significantly higher upfront material cost compared to carbon steel.
– Heavier, which may add to shipping and handling expenses.
– Difficult to machine, raising initial manufacturing complexity.
Application Impact:
Essential for pump housings, cutting heads, high-pressure fittings, and regions with poor water quality, such as some African and Middle Eastern locations.
International Buyer Considerations:
Widely preferred in European and Middle Eastern markets where compliance and longevity are prioritized. Ensures compatibility with international standards, often a requirement in export-oriented sectors. In some emerging markets, careful sourcing is required to avoid counterfeit or substandard grades.
Carbon Steel (e.g., ASTM A105, A216 WCB)
Key Properties:
Carbon steels are robust and widely available, providing high tensile strength and acceptable pressure ratings for non-corrosive water systems. While less resistant to corrosion, they can be coated or treated to enhance longevity.
Pros:
– Very cost-effective—excellent for price-sensitive markets.
– High mechanical strength for frame and low-risk componentry.
– Straightforward to fabricate, repair, or locally source.
Cons:
– Poor corrosion resistance without proper coatings or inhibitors.
– Susceptibility to pitting or rust in poor water conditions shortens lifespan.
– May require frequent maintenance or replacement.
Application Impact:
Common in structural frames, non-wetted housings, and budget-driven installations in stable indoor environments.
International Buyer Considerations:
Favored in South America and Africa where up-front cost is highly scrutinized and supply chains are mature. However, longer-term TCO may be higher where water purity is not reliably maintained.
Specialty Alloys (e.g., Inconel 625, Super Duplex Stainless)
Key Properties:
Specialty alloys like Inconel or Super Duplex stainless offer extreme corrosion resistance—standing up to highly saline, mineralized, or recycled process water. They maintain mechanical integrity under continuous high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
Pros:
– Superior chemical and wear resistance extends service life significantly.
– Can handle extreme operational demands (pressure, temperature, abrasive media).
– Meet stringent regulations in nuclear, oil & gas, chemical process sectors.
Cons:
– High to very high initial cost and variable global availability.
– Complex fabrication requires advanced manufacturing capabilities.
– Limited local suppliers in several emerging markets.
Application Impact:
Ideal for cutting heads, nozzles, and wetted components in industrial zones with challenging water profiles, or where downtime must be minimized.
International Buyer Considerations:
Essential for exports to Europe or for Middle Eastern companies dealing with brackish water or aggressive process chemicals. Buyers should verify certifications and traceability (EN10204, ASME BPE) to ensure compliance and avoid counterfeit materials.
Reinforced Polymers (e.g., PTFE, PEEK composites)
Key Properties:
Advanced polymers and composites like PTFE (Teflon), PEEK, or glass-fiber-reinforced plastics provide low-friction, self-lubricating surfaces with good corrosion resistance. Not typically load-bearing, but excellent for gaskets, seals, and non-wetted internal guides.
Pros:
– Non-corrosive and lightweight, reducing overall machine mass.
– Excellent chemical resistance and flexibility for intricate seals.
– Lower overall cost for non-critical parts.
Cons:
– Unsuitable for primary structural or high-pressure components.
– Mechanical strength and temperature tolerance below metals.
– Degradation possible with some aggressive abrasive media.
Application Impact:
Used primarily for seals, bushings, and specialized fittings where chemical inertness or low friction is paramount.
International Buyer Considerations:
Readily available globally, but buyers in Africa and South America should ensure compatibility with local water chemistries. Sourcing from ISO/ASTM-certified suppliers is key for quality assurance.
Comparative Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for water jet cutting machine cost | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel (e.g., 304/316) | Pump housings, high-pressure lines, wetted parts in harsh environments | Excellent corrosion resistance, global standards | Higher upfront cost, heavier, difficult to machine | High |
| Carbon Steel (e.g., ASTM A105/WCB) | Structural frames, low-cost system components in non-corrosive settings | Very cost-effective, easy to source and fabricate | Poor corrosion resistance unless coated, higher TCO in harsh environments | Low |
| Specialty Alloys (e.g., Inconel, Super Duplex) | Cutting heads, nozzles, high-wear parts under extreme conditions | Extreme durability and chemical resistance | Very high cost, complex sourcing and fabrication | High |
| Reinforced Polymers (e.g., PTFE, PEEK) | Seals, bushings, non-load-bearing guides | Non-corrosive, lightweight, low maintenance | Not suitable for primary structural/high-pressure parts | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for water jet cutting machine cost
Precision Engineering and the Water Jet Cutting Machine Production Lifecycle
A water jet cutting machine is a highly engineered asset that combines advanced hydraulics, microelectronics, and precision fabrication. For international B2B buyers—especially those coordinating cross-border investment—understanding the full manufacturing and quality assurance process is critical for evaluating a machine’s total cost, reliability, and lifecycle value. This knowledge not only safeguards capital expenditure but directly impacts operational uptime and competitive capability.
Stages of Water Jet Cutting Machine Manufacturing
The creation of a high-performance water jet cutting machine typically follows a sequence of tightly controlled manufacturing steps. Each stage aims to ensure the consistency, accuracy, and durability necessary for rigorous industrial use.
1. Material Preparation and Sourcing
Key Actions:
– Selection of Raw Materials: Sourcing high-grade stainless steel, precision alloys, and composite components suited for high-pressure systems and corrosion resistance.
– Supplier Vetting: Materials are procured from qualified suppliers; certificates of conformance and pre-shipment inspection reports are often mandated.
– Incoming Inspection: All materials undergo thorough dimensional, chemical, and mechanical property checks before entering the production line.
B2B Action Point: Request documentation on raw material provenance and ensure traceability down to heat/batch number, especially if importing into regions with stringent compliance (e.g., the EU, Turkey).
2. Component Fabrication and Forming
Key Techniques:
– CNC Machining: Precision parts (pump housings, cutting heads, and manifolds) are produced using multi-axis CNC machining to maintain tight tolerances, essential for ultra-high-pressure hydraulics.
– Surface Treatments: Critical components receive anti-corrosion coatings, hardening, or specialized finishes to extend lifespan.
– Pressure Vessel Manufacture: For intensifiers and high-pressure lines, manufacturers typically follow ASME or relevant European Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) standards.
B2B Action Point: Verify that suppliers use state-of-the-art CNC facilities and have processes in place for validating surface finish and tolerance via Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM).
3. Assembly and Subsystem Integration
Key Steps:
– Sub-assembly Testing: Pumps, control panels, motion systems, and abrasive handling modules are initially assembled and undergo in-process checks.
– Main Assembly: Integration of all subsystems into the main frame; wiring of sensors, actuators, and controllers.
– System Calibration: Initial calibration of hydraulic, pneumatic, and control circuits to specified operational parameters.
B2B Action Point: Insist on visibility into assembly line processes and calibration procedures. For remote sourcing (e.g., from Asia to Africa or South America), request comprehensive assembly checklists and pre-dispatch testing evidence.
4. Finishing and Final Testing
Key Activities:
– Protective Finishes: Application of specialized industrial paints or coatings, especially for machines destined for humid or corrosive environments.
– Final System Testing: Complete machines are operated under load, cutting sample materials to validate accuracy, speed, pressure holding, and cut quality.
– Packing and Preservation: Export jobs receive moisture-proof, shock-protected packaging suitable for long-distance transit and local storage conditions.
B2B Action Point: Include specific finish and packaging requirements in your procurement contract, especially for installations in climates subject to high humidity or temperature extremes (e.g., South Africa, UAE).
Quality Control (QC) Frameworks and Best Practices
Reliable water jet cutting machines result from robust, multi-tiered quality assurance systems. Global buyers should be intimately familiar with the following checkpoints and standards.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
- ISO 9001: Universal benchmark for quality management systems; ensures consistent manufacturing and documentation practices. Most reputable manufacturers are certified.
- CE (European Conformity): Compliance is legally required for machinery entering the EU, signifying adherence to health, safety, and environmental regulations.
- Other Regional Standards: Depending on the application and country, look for UAE ESMA, SASO (Saudi Arabia), EAC (Eurasian Economic Union), or South African NRCS where relevant.
- Application-Specific Standards: For sectors like aerospace, automotive, or oil & gas, look for compliance with API, ASME, or sectoral norms.
B2B Action Point: Request copies of relevant certifications and audit summaries. Validate their current status using official registries.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
- IQC (Incoming Quality Control): Ensures that all sourced materials/components meet the required standard before assembly.
- IPQC (In-Process Quality Control): Real-time inspections throughout the manufacturing and assembly stages—includes dimensional checks, pressure tests, and electrical integrity checks.
- FQC (Final Quality Control): Rigorous machine-level assessments at end-of-line covering operational testing, leak detection, accuracy validation, and safety compliance.
Typical Testing Methods for Water Jet Machines
- Hydrostatic Pressure Testing: Verifies pressure vessel and piping integrity at or above working pressure.
- Dimensional and Geometric Analysis: Utilizes CMMs and laser measuring tools for high-precision parts.
- Electrical and Automation Testing: Checks all sensor/actuator responses, safety interlock function, and CNC interface reliability.
- Cut Quality Testing: Assesses kerf width, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy across various materials and thicknesses.
- Abrasive Feed Performance: Tests metering and delivery precision under different load and humidity conditions.
B2B Action Point: Request detailed Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) protocols and corresponding test results for each delivered unit.
Verifying Supplier Quality: Practical Steps for Global B2B Buyers
The complexity of cross-border purchases—especially for Africa, South America, and the Middle East—demands additional diligence to mitigate risk and ensure delivered quality.
Actions to Ensure Reliable Quality
-
On-Site Audits and Inspections
Engage local agents, trusted certification bodies, or respected third-party inspection firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV Rheinland, Bureau Veritas) to audit the supplier’s facility prior to placing a major order. -
Third-Party Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI)
Mandate a PSI that covers functional testing, documentation review, and packaging verification before machines ship. -
Review Supplier QC Documentation
Obtain and critically examine quality control records—IQC/IPQC/FQC reports, test logs, and maintenance records. For machines in highly regulated sectors or export to the EU, this is especially crucial. -
Request for Detailed Certification Packages
Certificates should not only state compliance (e.g., with ISO 9001, CE) but also provide up-to-date, uniquely numbered copies traceable to independent audits. -
Virtual Acceptance and Remote FAT
For long-distance deals, arrange live video demonstrations of the whole factory acceptance test, including cut-sample validation using supplied part drawings.
Navigating Regional QC and Certification Issues
- Africa and South America: Some local regulatory frameworks remain in flux. Partner with customs specialists to ensure timely certification recognition and support from original equipment manufacturers.
- Middle East (e.g., Turkey, UAE): Ensure full alignment with local standards, which often blend EU and region-specific requirements. ESMA/CE and electricity grid compatibility must be double-checked.
- Europe: Machines must comply with CE, Machinery Directive, and potentially local workplace safety guidelines.
B2B Action Point: Insist on machine documentation in local languages (or English plus your own) to simplify customs clearance and end-user onboarding.
A clear command of the manufacturing and quality assurance processes for water jet cutting machines yields a purchasing edge, reduces post-installation disruptions, and ensures compliance with destination market standards. By rigorously auditing your supply chain and leveraging global best practices, you lay the foundation for maximum ROI and sustained operational excellence, whether sourcing from China for Johannesburg, or importing world-class equipment into Istanbul, São Paulo, or beyond.
Related Video: WATER JET MACHINE PROCESS : Working of abrasive water Jet machining process (animation).
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for water jet cutting machine cost Sourcing
Key Components of Water Jet Cutting Machine Costs
When sourcing a water jet cutting machine internationally, buyers must account for a comprehensive range of direct and indirect costs. Understanding these breakdowns is essential for accurate budgeting and supplier negotiations.
1. Materials & Core Components:
– Machine Body & Frame: Constructed primarily from high-grade steel or aluminum, these determine mechanical integrity and reliability.
– High-Pressure Pump & Intensifier: Often the most costly subsystem, requiring precision engineering and robust materials.
– Cutting Head & Nozzles: Consumable elements like sapphire or diamond nozzles, plus mixing chambers and abrasive delivery lines, necessitate regular replacement.
– CNC Controller & Electronics: Integrated motion controls and panels add to the bill of materials, with costs varying by automation level.
2. Manufacturing Overhead & Assembly:
– Labor: Skilled assembly, testing, and calibration drive labor costs—particularly for advanced, multi-axis or customized machines.
– Tooling & Fixtures: Initial investment in jigs, fixtures, and molds is amortized over production but adds upfront cost, especially for highly customized orders.
– Quality Control (QC): Stringent QC (pressure tests, accuracy checks, performance trials) increase labor hours and require specialized technicians.
– Overhead: Facility, utilities, equipment depreciation, and in-process waste are allocated per unit.
3. Operation-Linked Costs:
– Consumables: Garnet abrasive, high-pressure seals, water, and power are ongoing operating expenses—significant in abrasive-type units, less in pure water jets.
– Maintenance Parts: Pumps, seals, and cut heads need regular servicing. Local parts availability is vital, especially in regions where import delays are common.
4. Logistics & Importation:
– Shipping: Will vary by origin, machine weight/dimensions, and chosen Incoterm (e.g., EXW, FOB, CIF).
– Duties & Insurance: Import duties, customs clearance expenses, and cargo insurance all add to the landed cost, and rates differ regionally.
– Local Transport & Installation: Final-mile logistics, customs brokerage, and site assembly may add substantial costs, particularly in developing infrastructure environments.
5. Supplier Margin & Value-Added Services:
– Includes supplier’s profit, but also after-sales support, training, warranty, and spare parts provisioning. These services can be indispensable in Africa, South America, and remote Middle Eastern markets.
Primary Price Influencers in International Sourcing
Order Volume / MOQ
Larger batch orders usually lower per-unit price, but high MOQs may not align with all buyers’ CAPEX plans. Bulk deals yield the strongest negotiation leverage.
Specifications & Customization
Custom table sizes, automation level (3-axis vs. 5-axis), and brand-name pumps (KMT/Flow vs. local) can impact base price by 10–40%. Special requirements for software, enclosures, or local voltage standards add further cost.
Material Grades & Build Quality
Top-tier materials enhance durability but escalate both initial price and replacement part cost. Lower up-front prices may mean higher maintenance costs later.
Certification & Compliance
Machines with CE, ISO9001, or niche certifications (food-grade, aerospace) often cost more but are vital for regulated industries in Europe and the Middle East.
Supplier Reputation & Support
Established manufacturers may charge a premium, but international buyers benefit from proven reliability, faster parts supply, and robust after-sales service—a critical factor where local technical support is limited.
Incoterms & Logistics Arrangements
Supplier quotes vary significantly based on responsibility for freight, insurance, and import taxes. CFR/CIF pricing simplifies importing but limits buyer’s shipping control. EXW may lower the quote but leaves logistics management and risk to the buyer.
Cost Management Strategies and Buyer Recommendations
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Go beyond the purchase price. Model the running costs—particularly consumables, service intervals, and energy efficiency—relevant for local utility rates and supply chains.
- Negotiate Over Value, Not Just Price: Seek bundled offers (training, starter spares, extended warranty) rather than pushing solely for discounts. Emphasize long-term partnership, especially if the supplier provides in-region technical support.
- Assess Local After-Sales Ecosystem: Confirm spare part lead times and technician availability; delays in Africa or the Middle East with non-local suppliers can mean costly downtime.
- Leverage Regional Group Buys or Partnerships: Pooling orders with regional peers (e.g., industrial parks, trade associations) can improve pricing and encourage suppliers to invest in local support.
- Compare Multiple Incoterm Offers: Factor true landed costs, including exposure to logistics risks and customs duties.
Disclaimer:
All referenced costs and pricing variables are indicative and may fluctuate based on global market shifts, currency rates, freight conditions, and individual supplier arrangements. Consult suppliers and regional authorities for precise, up-to-date quotations.
Spotlight on Potential water jet cutting machine cost Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section offers a look at a few manufacturers active in the ‘water jet cutting machine cost’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct their own extensive due diligence before any engagement. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
27 Waterjet Cutting Machine Manufacturers in The World (swaterjet.com)
Located at the intersection of global sourcing and technical expertise, this detailed international ranking highlights 27 of the most reputable waterjet cutting machine manufacturers worldwide, curated for B2B buyers seeking high-value, cost-effective solutions. The guide aggregates options across Europe, Asia, and North America, focusing on companies offering CNC waterjet cutters, UHP pumps, and related advanced industrial equipment. Many of these manufacturers display proven track records in the production of pure water and abrasive waterjet machines, catering to diverse sectors such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and fabrication.
Key strengths include broad product portfolios, ranging from standard gantry-style and 3-axis cutters to specialized ultrasonic, laser, and compact waterjet systems. Several highlighted companies are recognized for their strong international sales channels—serving importers and distributors in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—with robust after-sales support networks. While specifics on certifications (such as ISO 9001) and unique technological differentiators vary, the listed manufacturers are generally noted for reliability, flexibility in customization, and competitive total cost of ownership. This resource serves as an essential starting point for buyers aiming to benchmark global suppliers and shortlist partners best aligned with regional compliance and application demands.
How Much Does a Water Jet Cutting Machine Cost (cuttingmachines.direct)
How Much Does a Water Jet Cutting Machine Cost (cuttingmachines.direct) positions itself as a key resource for businesses evaluating water jet cutting investments across diverse sectors. The company provides transparent cost analysis, with machines typically ranging from $50,000 for basic models to $500,000 for high-capacity, industrial-grade systems. Their market guidance emphasizes total cost of ownership—highlighting ongoing operational expenses, such as consumables (abrasives, water, electricity) averaging $15–$30 per hour, and the critical impact of maintenance on long-term efficiency. Buyers are advised on machine selection tailored to specific materials and applications (e.g., abrasive vs. pure water), strategies for reducing consumable use, and the value of investing in quality abrasives and reliable filtration. While publicly available details about manufacturing capabilities and certifications are limited, their content demonstrates a strong understanding of the international B2B procurement process, especially for buyers navigating complex import requirements in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Much Does Water Jetting Cost (www.fedjetcutting.com)
How Much Does Water Jetting Cost, operated under the Fedjet Cutting brand, positions itself as a supplier with a diversified waterjet product portfolio, including CNC, PowerJet, SmartJet, and robotic waterjet cutting series. The company differentiates by providing options tailored for various industrial applications—ranging from standard sheet processing to advanced robotic solutions—addressing both entry-level and sophisticated manufacturing needs. Fedjet emphasizes modular machine architecture and a dedicated focus on high-performance intensifier pumps, which can contribute to optimized operating costs and maintenance for international buyers.
Though public details on certifications or manufacturing capacity are limited, Fedjet is recognized for transparent cost breakdowns and market comparisons, helping B2B purchasers benchmark capital expenditure and anticipate total cost of ownership. Its apparent engagement with global pricing analysis signals familiarity with international procurement requirements, which is pertinent for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seeking both product versatility and cost clarity.
Quick Comparison of Profiled Manufacturers
| Manufacturer | Brief Focus Summary | Website Domain |
|---|---|---|
| 27 Waterjet Cutting Machine Manufacturers in The World | Curated global manufacturers, broad product range | swaterjet.com |
| How Much Does a Water Jet Cutting Machine Cost | In-depth waterjet cost guidance for global buyers | cuttingmachines.direct |
| How Much Does Water Jetting Cost | Diverse waterjet lineup, cost transparency, global outlook | www.fedjetcutting.com |
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for water jet cutting machine cost
Key Technical Specifications Impacting Water Jet Cutting Machine Costs
When evaluating water jet cutting machine investments, understanding the specifications that influence both operational effectiveness and total cost of ownership is crucial for B2B buyers across international markets. Here are several pivotal properties to examine:
-
Pressure Rating (PSI/bar):
The maximum operating pressure, often between 40,000 – 90,000 PSI (2,800 – 6,200 bar), directly impacts the machine’s cutting capability and throughput. Higher pressures allow for faster cutting and the ability to process thicker or harder materials but generally result in higher initial equipment and ongoing maintenance costs. Matching pressure ratings to your production needs optimizes ROI. -
Cutting Head Configuration:
Machines offer pure water or abrasive heads, and some are convertible. Abrasive heads significantly increase versatility—enabling processing of metals, stone, and ceramics—while pure water is ideal for soft materials. For B2B buyers, the ability to switch or maintain multiple heads can expand service offerings and accommodate changing project portfolios. -
Table Size and Axis Control:
Worktable dimensions (e.g., 2500 mm x 1500 mm) and axis capabilities (typically 3-axis for flat, 5/6-axis for 3D) dictate the maximum part size, shape complexity, and range of applications the system can handle. A larger table and more axes enable greater productivity and adaptability, but also raise system costs and space requirements. -
Tolerance and Precision:
Stated as ±0.05–0.2 mm for most industrial units, this measures the system’s ability to maintain dimensional accuracy. Tighter tolerances are vital for technical fields like aerospace or automotive, where cutting precision directly influences fit and assembly. Higher-precision machines tend to be more expensive but can reduce downstream machining and waste. -
Pump Type and Reliability:
Intensifier and direct-drive pumps differ in efficiency, service intervals, and energy usage. The right choice affects lifespan, availability of local spare parts, and ease of maintenance—all significant to international buyers where technical support or parts logistics can be challenging. -
Consumable and Utility Consumption:
Specifications for garnet abrasive (kg/hr), electricity (kW), and water (L/hr) inform ongoing operating costs. Machines with efficient, easy-to-source consumables will yield more predictable expenditure—a key concern in regions facing fluctuating utility costs or import restrictions.
Trade and Industry Terminology Every B2B Buyer Should Know
Global procurement of water jet cutting machinery relies on clear understanding of essential terms used in supplier negotiations, purchase agreements, and international logistics. Below are vital trade and technical terms to master:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
Indicates the company that originally produces the machine or core components. Knowing whether you’re dealing with an OEM or a third-party reseller can impact access to support, warranties, and the latest technology. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
Refers to the lowest number of units or combined value a supplier will accept per order. Understanding MOQ is essential when budgeting for capital equipment, especially if interested in optional accessories or spare parts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation):
A formal process used to solicit price and terms from multiple suppliers. A detailed RFQ—stating technical specifications, performance needs, and required certifications—ensures you receive apples-to-apples pricing for better decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms):
A global standard defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, import duties, and risk transfer in cross-border deals (e.g., FOB, CIF, DAP). The selected Incoterm will impact your landed cost and should be factored into your total procurement budget. -
Lead Time:
The period from order confirmation to machine delivery (and possibly installation). Longer lead times may affect project scheduling or equipment changeover plans, particularly for buyers in remote or emerging markets. -
After-Sales Service Agreement:
Outlines the scope, response time, and costs of post-purchase technical support, training, and spare parts provision. For international B2B buyers, robust after-sales support is critical for minimizing downtime and operational risk.
By focusing on these technical parameters and mastering key trade terms, international buyers can confidently assess total cost, negotiate effectively, and secure the right water jet cutting solutions tailored to their demanding industrial needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the water jet cutting machine cost Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The water jet cutting machine sector is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by automation, digitalization, and the global push for operational efficiency. International B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are witnessing rising demand for precision-cutting across sectors such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and heavy industry. As these economies strive to modernize manufacturing capabilities, water jet cutting machines present an attractive option due to their ability to process a diverse range of materials—metals, composites, glass, ceramics, and advanced plastics—without introducing heat-induced warping or chemical contamination.
Among key market dynamics, cost transparency and total cost of ownership (TCO) are increasingly prioritized. Buyers favor machines with clear operational cost structures, factoring in equipment depreciation, consumable usage (such as abrasives and nozzles), labor, and energy. This is especially important in regions with fluctuating currency values and variable input costs. B2B procurement teams are also leveraging online calculators and simulation tools to anticipate long-term costs—a growing trend as buyers seek to optimize ROI under constrained budgets.
Supplier ecosystems are broadening, with a notable shift towards hybrid sourcing: combining established global brands with competitive regional manufacturers—most notably from China and Turkey. For buyers in emerging markets like South Africa or Brazil, this facilitates both access to advanced technology and local service/support networks. Additionally, modular and portable water jet cutter options are gaining traction, particularly among smaller factories and job shops aiming for scalability without heavy up-front investment.
From a technology standpoint, there is a steady adoption of CNC automation (3-, 5-, and 6-axis systems) for complex shapes and greater repeatability, as well as integration with digital manufacturing workflows. Data-driven maintenance and remote monitoring are also emerging trends, helping international buyers minimize downtime and reduce operational risk.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is moving to the forefront of sourcing decisions in the water jet cutting machine industry. The technology itself is inherently eco-friendlier than many thermal cutting methods: it produces no harmful fumes, minimizes hazardous waste, and allows for precise water and abrasive usage (with many modern units offering recycling systems for water and granulate reuse). For buyers in Europe and increasingly in the Middle East and South America, environmental compliance is not just a regulatory issue but a market differentiator, supporting green certifications and improving stakeholder trust.
Ethical sourcing now extends from machine procurement to consumables and service agreements. B2B buyers are increasingly auditing supply chains for responsible sourcing of abrasives (such as garnet), ensuring these do not contribute to environmental degradation or unethical labor practices. Partnering with suppliers who provide transparency around their manufacturing processes, offer ISO 14001 (environmental management) or similar certifications, and use recyclable or reusable materials can substantially reduce ESG (environmental, social, governance) risk.
Additionally, regional government incentives—such as tax breaks on energy-efficient machinery or import advantages for sustainable tech—are influencing purchasing strategies, particularly in the EU and parts of Africa. Buyers should also prioritize equipment with digital energy management features, low water consumption profiles, and upgradable components. This not only aids in reducing environmental impact but also provides long-term cost savings through improved efficiency and lower waste.
Brief Evolution and B2B Significance
Water jet cutting technology originated in the mid-20th century, initially using pure water streams for paper and soft material processing. The breakthrough came with the introduction of abrasive water jets, enabling efficient slicing of metals and hard composites. What began as niche equipment for high-value manufacturing has since evolved into a cornerstone of modern global production.
Today’s systems integrate advanced CNC motion, precision pumps, and automated monitoring, empowering B2B buyers to achieve levels of quality and versatility unattainable through traditional methods. The sector’s evolution has expanded accessibility—both in cost and technical support—enabling businesses in emerging regions to leapfrog older technologies and compete in high-value supply chains. For international buyers, understanding this historical trajectory underscores the value of strategic investment in water jet solutions as a foundation for globally competitive manufacturing.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of water jet cutting machine cost
-
How can I ensure the credibility and reliability of international water jet cutting machine suppliers?
Vetting international suppliers requires multi-layered due diligence. Begin with a review of business licenses, company registration, and export experience. Request references from buyers in similar markets, and prioritize manufacturers with established export histories to Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe. Assess certifications (such as ISO, CE, or local standards), factory audit reports, and the ability to provide video walkthroughs or virtual inspections. Utilize third-party inspection agencies and consider trade assurance or escrow services to reduce risk during the transaction. -
What level of machine customization is typically offered for global buyers, and how does this impact cost?
Most reputable manufacturers allow B2B buyers to request modifications—such as increased cutting bed size, pump upgrades, regional voltage compatibility, or tailored software interfaces. Customization may also include integration with automation lines or local compliance adjustments. These changes influence total cost due to additional engineering and lower economies of scale, so buyers should specify requirements early and obtain detailed quotations. Clear documentation of technical needs and sign-off on engineering plans is essential before production commences. -
What is the standard minimum order quantity (MOQ), typical lead time, and recommended payment terms when buying water jet cutting machines internationally?
Unlike consumable products, MOQs for industrial machinery are often flexible—many suppliers accept even single-unit purchases, particularly for complex or high-value items. Standard lead times vary from 6 to 16 weeks, depending on level of customization and production backlog. For payment, expect to negotiate a deposit (typically 30%), with the balance due before shipment or upon inspection. Using irrevocable letters of credit (L/C) or secure platforms is advised, especially for first-time transactions or high-value orders. -
How should I verify quality assurance (QA) processes and certification compliance for imported machines?
Quality assurance starts with requesting documentation on factory QA/QC protocols, such as in-process checks, test-cutting videos, and final inspections. Insist on valid international certifications—CE marking (for European compliance), ISO 9001 (for quality management), and local certifications as mandated by your market (e.g., SABS in South Africa, GOST in certain Middle East countries). Arrange for independent pre-shipment inspection or remote third-party verification. Be sure certificates are up to date and—if applicable—aligned with local regulatory directories. -
What are the main logistics considerations when importing a water jet cutting machine, especially to Africa, South America, or the Middle East?
Consider the incoterms in your contract (FOB, CIF), as these define responsibility for freight, insurance, and customs clearance. Confirm that your supplier has experience shipping to your region, ideally with relevant references. Check if components may require special import licenses or adherence to national standards. Factor in port accessibility, warehousing, and local infrastructure for final delivery. Work with experienced freight forwarders and clarify responsibilities for offloading and installation upon arrival. -
How can disputes regarding machine quality, delivery delays, or non-conformance be resolved effectively across borders?
A robust, written purchase contract is critical; it should specify technical acceptance criteria, penalties for late delivery or non-conformance, and clear dispute resolution channels. Escrow or trade assurance services offer some protection for initial transactions. In case of quality issues, rely on independent inspection documentation and define remedial steps (replacement, repair, or credit). For complex disputes, designate a neutral arbitration venue and refer to international arbitration bodies (such as ICC or SIAC) in your contract to minimize jurisdictional uncertainties. -
Are spare parts, after-sales service, and technical support readily available for water jet cutting machines in my region?
Proactive suppliers maintain stock of common spare parts or have regional agents to minimize downtime. Confirm before purchase whether the supplier has local partnerships for after-sales support, or provides remote technical assistance via video calls and online diagnostics. For buyers in Africa, South America, or remote Middle Eastern regions, contractualize spare parts supply (a recommended initial kit) and training for local technicians. Prioritize vendors with established support channels and parts warehousing in or near your region. -
What are the key operational costs to factor in beyond initial purchase price when planning for long-term ownership?
In addition to the purchase price, factor in machine depreciation, import duties, shipping, insurance, installation and commissioning, operator training, and utility setup (water, electricity). Ongoing costs include consumables (abrasives, seals, nozzles), routine maintenance, critical part replacements, and periodic calibration. For abrasive water jet systems, abrasive supply logistics should be assessed locally. Evaluate total cost of ownership (TCO) over the expected 10+ year lifespan and confirm the supplier’s projected running costs align with independent industry benchmarks.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for water jet cutting machine cost
Key Takeaways for International B2B Buyers
Achieving cost-effective water jet cutting operations hinges on a clear understanding of both direct and indirect expenses—including equipment depreciation, consumable parts, labor, and ongoing operational requirements such as water, electricity, and abrasives. Differences in machine types (pure water vs. abrasive), regional accessibility of consumables, and supplier reliability all have direct impacts on your total cost of ownership and long-term competitiveness.
Strategic sourcing is vital; buyers who prioritize supplier credibility, after-sales service, and parts availability will be better positioned to control costs, reduce downtime, and ensure consistent production quality. Assessing regional market nuances—for example, importation hurdles in Africa, supplier networks in the Middle East, or advanced technical support in Europe—enables buyers to bypass common pitfalls and build resilient value chains.
Looking Ahead: Positioning for Sustainable Growth
As global manufacturing evolves and demand for high-precision, versatile fabrication increases, water jet cutting technology will play an ever-larger role in value-added production. International buyers are encouraged to regularly benchmark machine and consumable costs, foster close supplier relationships, and keep abreast of emerging innovations. Investing in training, predictive maintenance, and robust cost analysis tools will drive operational excellence and ROI. Now is the time to take a proactive approach—laying the groundwork for sustainable success in an increasingly competitive global marketplace.