Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Low Melting Point Metals For Casting
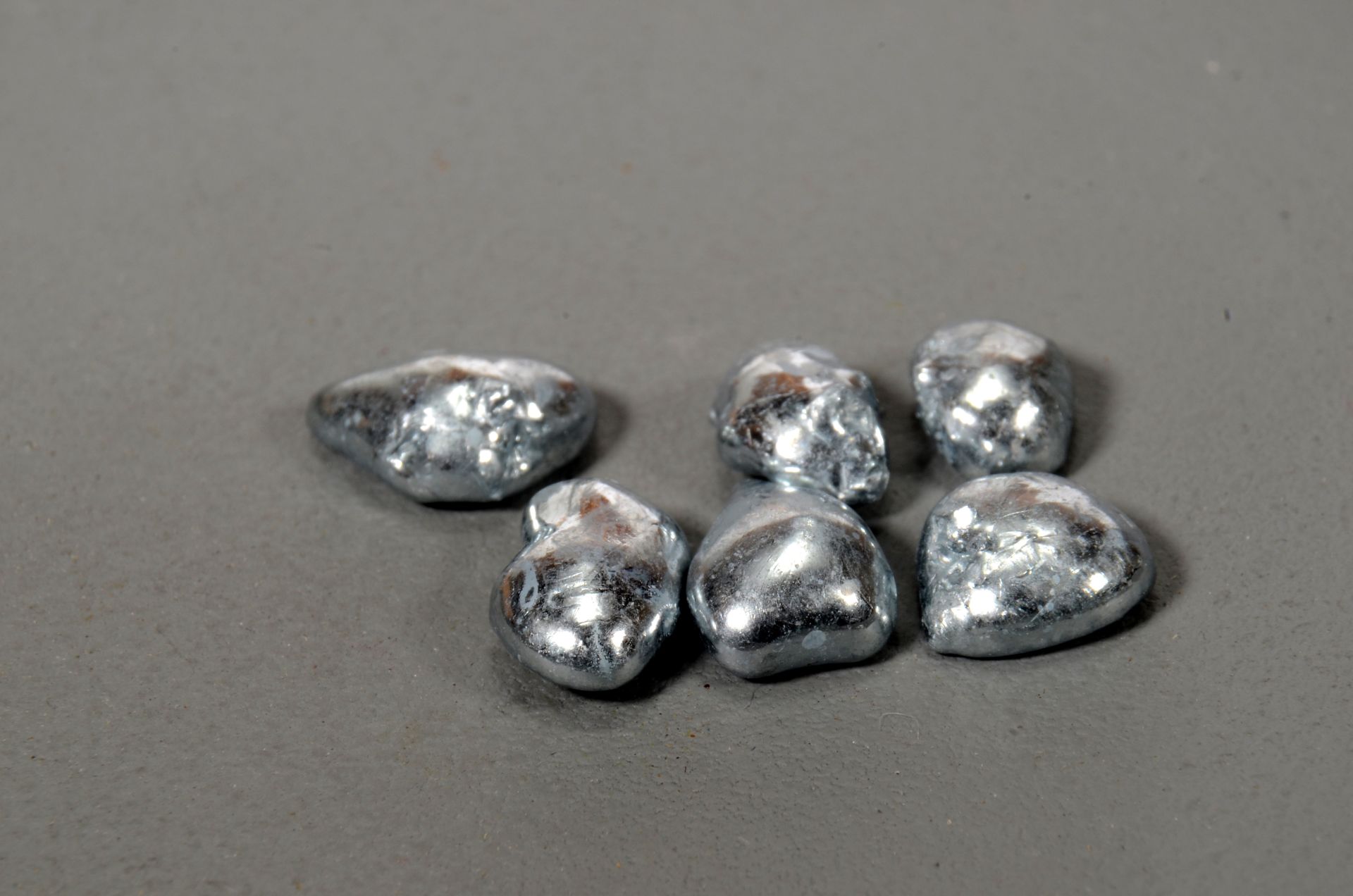

Manufacturing Insight: Low Melting Point Metals for Rapid Casting Applications
Low melting point metal alloys represent a critical capability in rapid prototyping and low-volume production, particularly where traditional casting methods prove impractical due to cost, lead time, or design complexity. At Shenzhen Honyo Prototype, we leverage these specialized materials to deliver functional prototypes and bridge production parts significantly faster than conventional aluminum or zinc die casting, eliminating costly steel tooling and extensive setup. These alloys, typically melting below 150°C, enable casting directly into silicone or epoxy molds derived from 3D printed patterns, making them ideal for validating designs, creating leak-testing fixtures, producing sacrificial cores, or manufacturing custom low-temperature soldering components. The inherent advantages—rapid solidification, minimal thermal stress on molds, and exceptional detail reproduction—accelerate iteration cycles while maintaining geometric fidelity essential for engineering evaluation.
Honyo Prototype’s expertise lies in optimizing this process for real-world manufacturing challenges. Our dedicated vacuum-assisted casting systems ensure complete mold fill and eliminate porosity, even in intricate geometries with undercuts or thin walls down to 0.5mm. We prioritize material compatibility and post-cast stability, rigorously controlling cooling rates to prevent segregation and ensure consistent mechanical properties. This precision is vital for applications requiring tight tolerances or direct interface with sheet metal assemblies, such as custom mounting brackets or thermal management components where low-melt inserts integrate seamlessly with stamped or formed housings. Unlike generalist prototyping services, Honyo provides integrated Design for Manufacturing (DFM) analysis specifically for low-melt casting, advising on draft angles, wall uniformity, and gating strategies to maximize part integrity and minimize secondary operations.
Our validated material portfolio balances performance with process efficiency. Key alloys and their typical applications are summarized below:
| Alloy Composition | Melting Range (°C) | Primary Applications | Honyo Process Advantage |
|————————|——————–|——————————————————-|———————————————|
| Bismuth-Tin (e.g., Cerrobend) | 70–74 | Sacrificial cores, low-temp solder seals, fixture masters | Vacuum degassing for zero porosity |
| Bismuth-Tin-Cadmium (e.g., Wood’s Metal) | 70–74 | Thermal cutoffs, fusible links, mold patterns | Controlled cooling to prevent segregation |
| Indium-Tin (e.g., Field’s Metal) | 62–64 | High-purity seals, semiconductor tooling, medical devices | Inert atmosphere handling for oxidation control |
Beyond material selection, Honyo’s value is rooted in actionable engineering support. We collaborate from the earliest design phase to determine if low-melt casting is optimal for your functional requirements, thermal constraints, and lifecycle expectations. Our 72-hour typical turnaround for mold creation and casting—from approved CAD to functional metal part—compresses development timelines without compromising on critical validation data. This capability is especially valuable when integrating cast components with sheet metal subassemblies, allowing engineers to verify fit, form, and function before committing to high-cost production tooling. For projects demanding rapid physical validation of metal components under realistic conditions, Honyo Prototype delivers the precision, speed, and material science expertise to de-risk your path to manufacturing. Contact our engineering team to discuss how low-melting point casting can accelerate your next prototype iteration.
Technical Capabilities
Low Melting Point Metal Casting in Sheet Metal Fabrication
At Shenzhen Honyo Prototype, our expertise in sheet metal fabrication extends to specialized processes involving low melting point metals for casting applications. These materials are particularly valuable in rapid prototyping, investment casting patterns, and temporary tooling, where precision, reusability, and ease of processing are critical. While traditional sheet metal operations such as laser cutting, bending, and welding are primarily associated with higher-strength metals like steel or aluminum, the integration of low melting point alloys enables hybrid manufacturing solutions—especially when used in conjunction with mold-making or sacrificial components.
Common low melting point metals used in our casting processes include alloys based on tin, lead, bismuth, and indium. These materials typically exhibit melting points below 300°C, allowing for safe handling and energy-efficient processing. Although these metals are not suitable for structural sheet metal components due to limited mechanical strength and thermal stability, they serve as excellent candidates for master patterns, foundry inserts, and low-volume casting molds. When combined with laser-cut steel or aluminum support structures, these castings can be precisely integrated into larger assemblies.
Laser cutting of low melting point metals is generally not recommended due to their thermal sensitivity; excessive heat input can lead to distortion, dross formation, or complete melting at the cut zone. Instead, we utilize laser cutting to fabricate containment jigs, mold frames, or alignment fixtures from stainless steel or mild steel, which are then used to support and shape the cast low-melting alloys. This indirect approach ensures dimensional accuracy and process stability.
Bending operations are similarly limited with low melting point metals due to their softness and low yield strength. However, we employ precision-formed sheet metal dies—laser-cut and CNC-bent—to cold-form or compress cast alloy components. This enables repeatable shaping without relying on post-cast mechanical manipulation of the soft metal.
Welding is not applicable to low melting point casting alloys in the traditional sense. Instead, we use mechanical fastening or epoxy joining when integrating these components with sheet metal subassemblies. For mold integration, we often encapsulate cast alloy sections within laser-welded steel housings to provide structural integrity and thermal management.
Our process tolerances are optimized for hybrid fabrication, balancing the precision of sheet metal forming with the fluid nature of low temperature casting. Below is an overview of key materials and achievable tolerances when used in conjunction with our laser cutting, bending, and support fabrication capabilities.
| Material | Melting Point (°C) | Typical Use Case | Laser Cutting Compatibility | Bending Compatibility | Welding Compatibility | Dimensional Tolerance (± mm) |
|———|——————–|——————|—————————–|————————|————————|——————————-|
| Tin-Bismuth (SnBi) | 138–170 | Casting patterns, mold inserts | Indirect (fixtures only) | Not recommended | Mechanical joining only | 0.15 |
| Bismuth-Tin-Lead (BiSnPb) | 95–150 | Low-volume casting molds | Indirect (fixtures only) | Not recommended | Mechanical joining only | 0.20 |
| Field’s Metal (BiPbIn) | 62–65 | Precision sacrificial cores | Indirect (fixtures only) | Not recommended | Mechanical joining only | 0.10 |
| Cerrolow 117 (BiInSn) | 47–70 | Temporary tooling | Indirect (fixtures only) | Not recommended | Mechanical joining only | 0.12 |
Through strategic integration of sheet metal fabrication and low melting point casting, Shenzhen Honyo Prototype delivers high-precision, functionally integrated components for advanced prototyping and specialized manufacturing applications.
From CAD to Part: The Process

Manufacturing Guide: Low Melting Point Metal Casting Workflow
At Shenzhen Honyo Prototype, our sheet metal fabrication expertise extends to specialized low melting point metal casting for rapid prototyping and low-volume production. This process leverages alloys such as Field’s metal, Wood’s metal, and bismuth-tin variants, which melt below 160°C, enabling cost-effective production of intricate geometries unsuitable for traditional sheet metal forming. Below is our streamlined workflow from CAD submission to finished part, optimized for speed and precision.
AI-Powered Quoting
Upon CAD file receipt, our proprietary AI quotation engine evaluates geometry, material selection, and volume requirements. The system cross-references historical casting data to predict solidification behavior, thermal stress points, and mold complexity. Critical parameters include wall thickness uniformity, undercuts, and parting line feasibility. Within 2 hours, clients receive a detailed quote outlining material costs, lead time (typically 3–7 days), and initial feasibility flags. This phase ensures alignment on technical constraints before proceeding, minimizing downstream delays.
DFM Analysis for Casting Integrity
Our engineering team conducts a rigorous Design for Manufacturing review focused on low-temperature casting physics. Key considerations include thermal contraction coefficients (0.03–0.05% for Bi-Sn alloys), mold venting for trapped gases, and strategic riser placement to prevent shrinkage cavities. We simulate solidification using Magmasoft® to identify hot spots and optimize cooling rates. Clients receive annotated DFM reports with actionable recommendations—such as adjusting fillet radii or adding draft angles—to enhance yield without compromising design intent. This step reduces iteration cycles by up to 70% compared to conventional casting approaches.
Production Execution
Approved designs move to production in our climate-controlled casting cell. Aluminum or silicone molds are prepared per DFM specifications, with vacuum-assisted pouring systems eliminating porosity. Molten metal (held at 70–150°C depending on alloy) is injected under 0.5–1.0 bar pressure to ensure cavity fill. Post-casting, parts undergo automated degating, vibratory tumbling, and dimensional validation via CMM. Final inspection includes X-ray porosity checks and surface roughness verification (Ra ≤ 3.2 μm). All processes comply with RoHS and REACH standards, with lead-free alloys as default.
Material and Process Specifications
| Alloy Type | Melting Range (°C) | Common Applications | Key Process Notes |
|——————|——————–|—————————-|———————————————–|
| Field’s Metal | 62–64 | Thermal fuses, molds | Requires inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation |
| Wood’s Metal | 70–74 | Medical devices, tooling | High bismuth content; slow cooling minimizes cracks |
| Bi-42/Sn-42 | 138–142 | Electronics housings | Optimal for thin walls (≥0.8 mm) |
| Cerrocast 136 | 136–140 | Prototyping, art casting | Low shrinkage (0.03%); minimal post-machining |
This integrated workflow ensures low melting point castings meet sheet metal assembly tolerances while accelerating time-to-prototype. By unifying AI-driven planning, physics-based DFM, and controlled production, Honyo delivers cast components with 95% first-pass yield for seamless integration into broader fabrication projects. Contact our engineering team to discuss alloy selection for your next prototype.
Start Your Project
Start Your Project with Precision Low Melting Point Metal Casting at Shenzhen Honyo Prototype
When it comes to prototyping and small-batch production involving intricate geometries and rapid turnaround, low melting point metal casting offers a strategic advantage. At Shenzhen Honyo Prototype, we specialize in advanced sheet metal fabrication integrated with precision casting techniques, enabling clients to develop functional prototypes and production-ready components efficiently. Our expertise in low melting point alloys ensures dimensional accuracy, excellent surface finish, and compatibility with secondary processes such as CNC machining, welding, and plating.
Low melting point metals—such as tin, bismuth, lead-based alloys, and their eutectic combinations—are ideal for applications requiring thermal fusibility, ease of rework, and minimal thermal stress on tooling. These materials are widely used in industries including electronics, aerospace, medical devices, and automotive R&D, where rapid iteration and cost-effective tooling are critical. Whether you’re developing conformal cooling inserts, sacrificial cores, or custom jigs and fixtures, our manufacturing solutions are engineered to meet exact specifications while accelerating your product development cycle.
We understand that every project begins with a concept—and transforming that concept into a tangible, high-performance component requires collaboration, technical insight, and responsive support. That’s why we invite you to start your project with our dedicated engineering team, led by Susan Leo, who brings over 12 years of experience in precision metal fabrication and prototype development.
Our facility in Shenzhen is equipped with controlled-atmosphere casting systems, precision molds, and post-processing capabilities to ensure consistency and repeatability. We adhere to strict quality control standards, including material certification and dimensional inspection, to guarantee performance under real-world conditions.
To ensure the best outcome for your application, we recommend early consultation to evaluate alloy selection, design for manufacturability (DFM), and integration with downstream processes. By engaging early, we can optimize your design for casting feasibility, minimize material waste, and reduce lead times.
Below are key specifications for commonly used low melting point alloys in our casting processes:
| Alloy Type | Melting Range (°C) | Typical Composition | Common Applications |
|———————-|——————–|—————————-|——————————————|
| Tin-Bismuth (Sn-Bi) | 138 – 170 | Sn 42%, Bi 58% | Electronics, thermal release layers |
| Bismuth-Tin-Lead | 95 – 140 | Bi 50%, Sn 27%, Pb 23% | Prototyping molds, low-stress tooling |
| Field’s Metal | 62 – 65 | Bi 32.5%, Pb 51%, Sn 16.5% | Safety devices, experimental tooling |
| Cerrotru | 160 – 175 | Pb 48%, Sn 47%, Cd 5% | Die casting inserts, temporary supports |
All materials are handled in compliance with RoHS and REACH standards where applicable, and we offer both leaded and lead-free options depending on regulatory and performance requirements.
Starting your project is simple. Contact Susan Leo directly at info@hy-proto.com to discuss your design, share CAD files, or request a quote. Our team responds within 24 hours to ensure your development timeline stays on track. With Shenzhen Honyo Prototype, you gain more than a manufacturer—you gain a technical partner committed to innovation, speed, and precision. Let us help you turn your vision into reality.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Get a rough estimate for CNC/3D Printing costs.









